Head-to-head study: Brintellix® (vortioxetine) vs the SNRI venlafaxine¹
임상 현장에서 MDD 치료에 있어서 가장 중요한 문제는 어떤 항우울제를 먼저 사용해야 하는 지, 그리고 반응이 없는 경우 어떻게 치료를 진행해야 하는 지를 아는 것입니다.1 Head-to-head study는 치료의 상대적인 유효성에 대해 더 우수한 정보를 제공할 수 있습니다.1
Brintellix®는 급성 MDD 환자 대상의 Head-to-head study에서 venlafaxine과 비슷한 유효성‡을 보였습니다1
Mean change in MADRS total score from baseline to week 8 (FAS, OC)
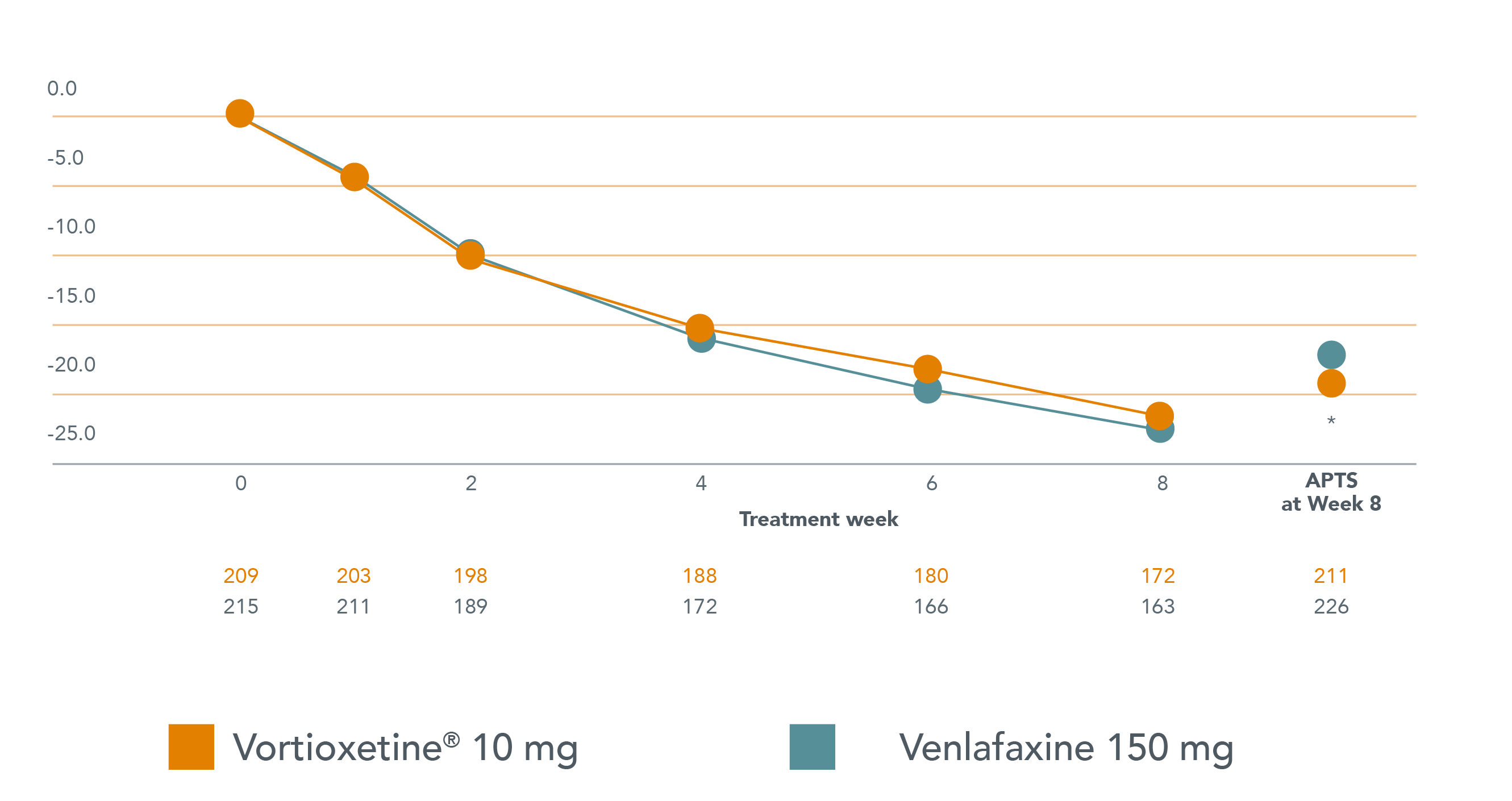
Adapted from Wang G et al. 2015.
Adapted from Wang G et al. 2015.

Brintellix® 투여 환자의 6.6%와 venlafaxine 투여 환자의 13.7%가 TEAEs로 인해 시험 참여를 중단했습니다.1
두 요법 모두에 대해 발생률 ≥5%인 이상사례에는 오심, 어지러움, 두통, 구강건조가 포함되었습니다. 또한, venlafaxine XR 투여 환자들은 추가로 우발적 과량투여, 식욕저하, 변비 및 불면증(≥5% 발생률)을 보고했습니다.1

‡ MADRS 총점으로 측정.
* venlafaxine 대비 p<0.05. APTS, 모든 투여된 환자군 (all patients treated set) - 요법을 1회 이상 투여받은 모든 환자 포함.
§ MADRS 에서 venlafaxine XR 대비 Brintellix® 의 통계적 및 임상적으로 유의한 이점 1.9 점 (p<0.05).1 두 활성 요법을 비교했을 때, MADRS 총점의 1점 차이는 임상적으로 관련이 있는 것으로 간주됨.2
Abbreviations:
APTS, all patients treated set; FAS, full analysis set; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale; MDD, major depressive disorder; OC, observed caases; SNRI, serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; XR, extended release.
‡ MADRS 총점으로 측정.
* venlafaxine 대비 p<0.05. APTS, 모든 투여된 환자군 (all patients treated set) - 요법을 1회 이상 투여받은 모든 환자 포함.
§ MADRS 에서 venlafaxine XR 대비 Brintellix® 의 통계적 및 임상적으로 유의한 이점 1.9 점 (p<0.05).1 두 활성 요법을 비교했을 때, MADRS 총점의 1점 차이는 임상적으로 관련이 있는 것으로 간주됨.2
Abbreviations:
APTS, all patients treated set; FAS, full analysis set; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale; MDD, major depressive disorder; OC, observed caases; SNRI, serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event; XR, extended release.

